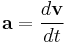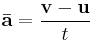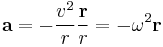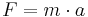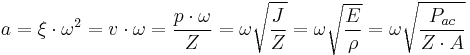Particle acceleration
In a compressible sound transmission medium - mainly air - air particles get an accelerated motion: the particle acceleration or sound acceleration with the symbol a in metre/second². In acoustics or physics, acceleration (symbol: a) is defined as the rate of change (or time derivative) of velocity. It is thus a vector quantity with dimension length/time². In SI units, this is m/s².
To accelerate an object (air particle) is to change its velocity over a period. Acceleration is defined technically as "the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time" and is given by the equation
where
- a is the acceleration vector
- v is the velocity vector expressed in m/s
- t is time expressed in seconds.
This equation gives a the units of m/(s·s), or m/s² (read as "metres per second per second", or "metres per second squared").
An alternative equation is:
where
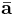 is the average acceleration (m/s²)
is the average acceleration (m/s²)
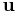 is the initial velocity (m/s)
is the initial velocity (m/s)
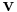 is the final velocity (m/s)
is the final velocity (m/s)
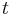 is the time interval (s)
is the time interval (s)
Transverse acceleration (perpendicular to velocity) causes change in direction. If it is constant in magnitude and changing in direction with the velocity, we get a circular motion. For this centripetal acceleration we have
One common unit of acceleration is g-force, one g being the acceleration caused by the gravity of Earth.
In classical mechanics, acceleration 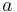 is related to force
is related to force 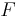 and mass
and mass 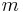 (assumed to be constant) by way of Newton's second law:
(assumed to be constant) by way of Newton's second law:
Equations in terms of other measurements
The Particle acceleration of the air particles a in m/s² of a plain sound wave is:
| Symbol | Units | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| a | m/s² | particle acceleration |
| v | m/s | particle velocity |
| ξ | m, meters | particle displacement |
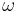 = 2 · = 2 · 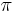 · f · f |
radians/s | angular frequency |
| f | Hz, hertz | frequency |
| p | Pa, pascals | sound pressure |
| Z | N·s/m³ | acoustic impedance |
| J | W/m² | sound intensity |
| E | W·s/m³ | sound energy density |
| Pac | W, watts | sound power or acoustic power |
| A | m² | area |